Industry Insights
Home > News > Industry Insight > Regulation of Serum Uremic Toxins by a Probiotic Composition and Its Applications
Regulation of Serum Uremic Toxins by a Probiotic Composition and Its Applications

Abstract
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a significant health concern characterized by the accumulation of uremic toxins in the blood, which are difficult to remove via dialysis. This study presents a novel probiotic composition, comprising Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LRa66 and Bifidobacterium bifidum BBi32, designed to regulate serum uremic toxins and alleviate CKD symptoms. The synergistic interaction between these two strains demonstrates a potential improvement in patients' clinical parameters, including reduced serum uremic toxin levels, blood pressure, and creatinine, alongside enhanced hemoglobin levels and intestinal barrier function.
Introduction
Uremic toxins such as indoxyl sulfate (IS), p-cresol glucuronide (PCG), and p-cresol sulfate (PCS) are predominantly derived from gut microbiota and are notoriously resistant to removal by conventional dialysis methods. This resistance exacerbates systemic inflammation and compromises gut barrier function in CKD patients, leading to the transfer of these toxins and bacteria into the bloodstream. Consequently, managing the gut microbiota to reduce the production of uremic toxin precursors represents a pivotal strategy in CKD treatment.
Methods
This research involved the cultivation and testing of two probiotic strains: Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LRa66 and Bifidobacterium bifidum BBi32. The strains were cultured, activated, and fermented. Post-fermentation, the cultures were centrifuged, mixed with lyophilization protectants, and freeze-dried to produce probiotic powders. These powders were then combined in various ratios to assess their efficacy in reducing uremic toxin levels and improving clinical outcomes in CKD.
Results
The probiotic composition exhibited the following outcomes:
1. Significant reduction in serum uremic toxin levels.
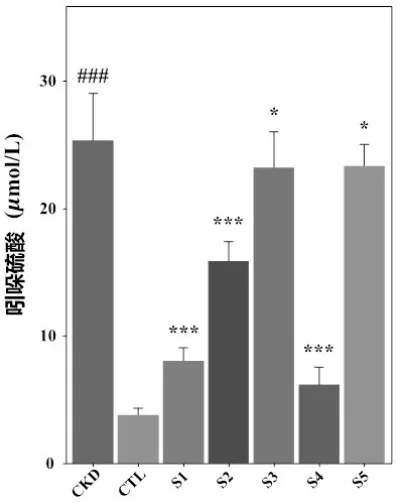
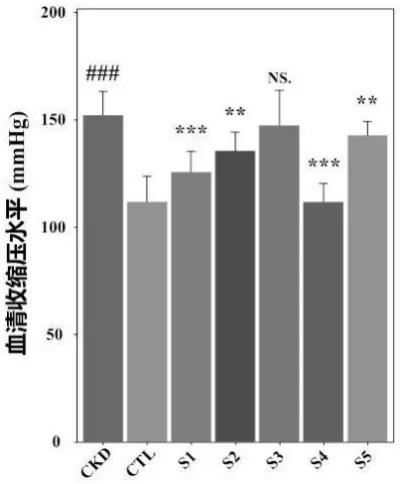
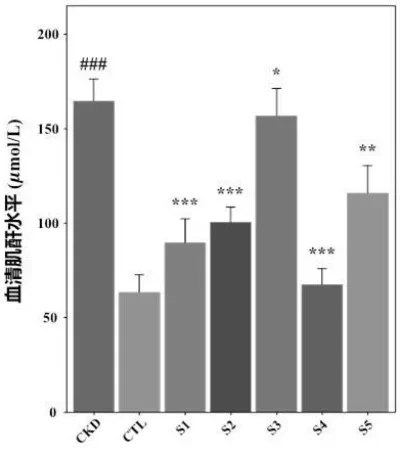
2. Decrease in systolic blood pressure and serum creatinine levels.
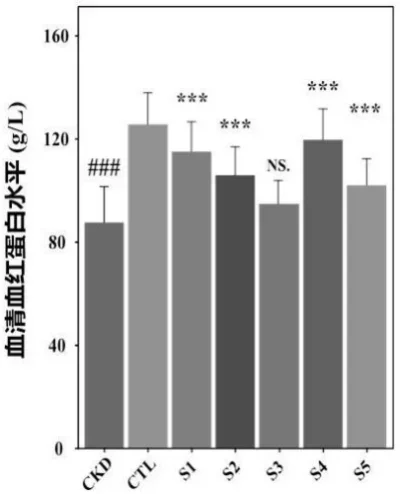
3. Increase in hemoglobin levels.
4. Improved intestinal barrier function in CKD patients.
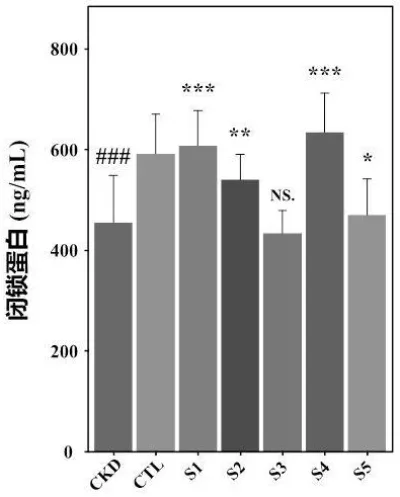
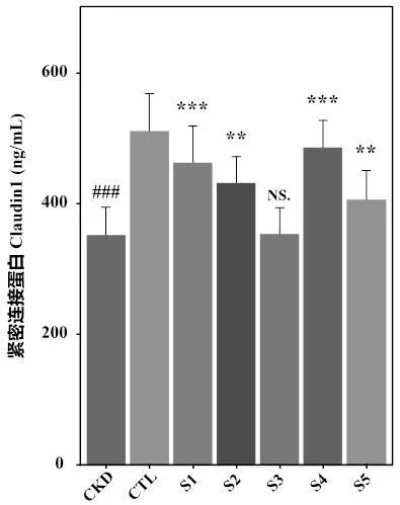
Discussion
The synergistic effect between Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LRa66 and Bifidobacterium bifidum BBi32 is evident in the enhanced therapeutic outcomes compared to individual strains. The combined probiotic not only reduced uremic toxins more effectively but also contributed to better overall health markers in CKD patients. This suggests that a dual-strain probiotic approach could offer a novel and effective treatment strategy for managing CKD.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that the combination of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LRa66 and Bifidobacterium bifidum BBi32 can significantly regulate serum uremic toxins and improve health outcomes in CKD patients. These findings support the development of new probiotic-based therapies for CKD management.
Keywords
Chronic Kidney Disease, Probiotics, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, Uremic Toxins, Gut Microbiota, Intestinal Barrier, Hemoglobin







 Leave a Message
Leave a Message Email
Email Linkedin
Linkedin