Industry Insights
Home > News > Industry Insight > WecMix™ Probiotic Formulation Containing WecLac® Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LRa05 in Osteoporosis Mitigation and Bone Health Enhancement
WecMix™ Probiotic Formulation Containing WecLac® Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LRa05 in Osteoporosis Mitigation and Bone Health Enhancement

Abstract
This probiotic patent focuses on a dual-strain formulation targeting osteoporosis improvement. The formulation contains Limosilactobacillus reuteri LR38 and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LRa05, which together exhibit synergistic effects on bone health by mitigating bone density loss and decreasing osteoclastogenic factors. These strains offer a potential solution for dietary supplement manufacturers aiming to enhance bone density, particularly beneficial for postmenopausal women.
Introduction
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by bone density reduction and increased fracture risk, is often exacerbated by the decline in estrogen, especially in postmenopausal women. Traditional treatments for osteoporosis have limitations and risks, making safe, natural alternatives highly desirable. This study introduces a probiotic formulation designed to address osteoporosis through gut microbiota modulation, promoting bone formation and reducing bone resorption.
Probiotic Strains:
1. Limosilactobacillus reuteri LR38 (CGMCC No.24408)
2. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LRa05 (CGMCC No.1.12734)
Mechanism of Action: The dual-strain composition acts on bone health through four main pathways:
· Bone Density Preservation: Reduces femoral and vertebral bone loss.
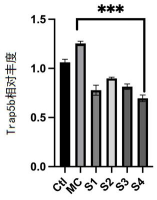
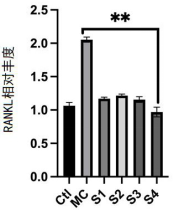
· Reduction in Osteoclastogenic Factors: Decreases markers like Trap5b and RANKL associated with bone resorption.
· Increase in Osteogenic Factors: Elevates levels of bone osteocalcin, which promotes bone formation.
· Reduction in CD4+ T Cell Production: Decreases osteoclast formation, essential for maintaining bone density.
Formulation and Dosage: The live probiotic count in the formulation is maintained at no less than 2×10^9 CFU/g, and the product can be delivered in forms such as freeze-dried powder, capsules, tablets, or granules. The formulation also includes excipients and stabilizers for enhanced efficacy and shelf life, such as gelatin, lactose, and various oligosaccharides.
Research Findings: The patent details an animal study demonstrating the effectiveness of the probiotic strains:
· Bone Volume (BV): Probiotics improved femoral and vertebral bone density by reducing osteoclast activity.
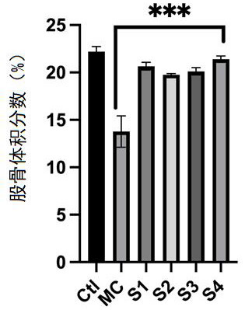
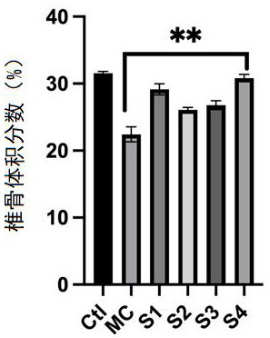
· Marker Reduction: Probiotic intervention decreased osteoclastogenic factors significantly while elevating osteogenic markers.
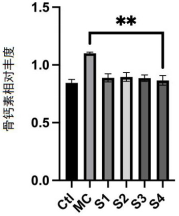
· T Cell Modulation: Probiotics effectively reduced CD4+ T cell production in the bone marrow, associated with reduced osteoclast activity.
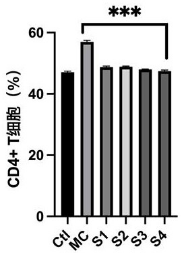
Conclusion: This probiotic formulation presents a novel solution for osteoporosis management by combining Limosilactobacillus reuteri LR38 and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LRa05, whose synergistic action enhances bone density and reduces osteoclast formation. The safe and effective composition makes it an attractive addition to dietary supplements targeting bone health, especially for individuals susceptible to osteoporosis, such as postmenopausal women.








 Leave a Message
Leave a Message Email
Email Linkedin
Linkedin